
Mastering Kling Motion Control: The Ultimate Guide to AI Digital Puppetry (2026)
[!NOTE] This guide is based on the official Kling AI Motion Control documentation as of January 2026.
Mastering Kling Motion Control: The Ultimate Guide to AI Digital Puppetry (2026)
In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI video generation, Kling Motion Control represents a paradigm shift from stochastic generation to deterministic control. This technology transforms how creators approach digital puppetry, offering unprecedented precision in character animation and movement replication. Unlike traditional AI video tools that rely on chance, Kling Motion Control provides a systematic framework for achieving consistent, high-quality results.
Motion Control vs. Motion Brush: Knowing the Difference
The distinction between Kling Motion Control and motion brush technologies is fundamental to understanding their respective applications. Motion Control operates on a skeleton-driven approach, where the AI analyzes the underlying bone structure and joint movements from reference footage. This method excels at replicating complex physical actions with anatomical accuracy.
In contrast, motion brush tools follow trajectory-driven patterns, focusing on the path of movement rather than the structural mechanics. While effective for simple animations, they lack the precision required for realistic human motion replication. The Kling Motion Control system's ability to understand biomechanics makes it particularly valuable for applications requiring natural movement patterns.
Deep Dive: The Two Character Orientation Modes
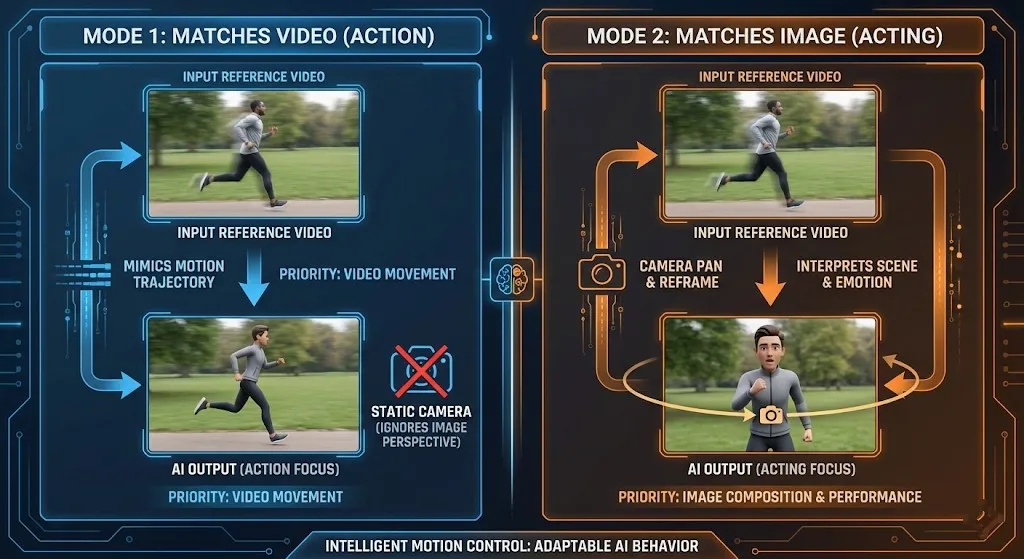
Mode 1: Character Orientation Matches Video (Best for full-body action, sports)
This default mode prioritizes maintaining the spatial relationship between the character and their environment as seen in the reference video. When you select Character Orientation Matches Video, the AI preserves the original camera perspective and character positioning relative to the background. This approach is ideal for:
- Sports sequences where maintaining field orientation is crucial
- Dance performances requiring consistent stage positioning
- Action scenes with complex environmental interactions
- Group activities where spatial relationships matter
The system analyzes the reference video's camera angles and character placement, then applies these spatial constraints to your generated content. This ensures that movements remain contextually appropriate within their virtual environment.
Mode 2: Character Orientation Matches Image (Best for acting, camera moves)
When you choose Character Orientation Matches Image, the system prioritizes your character's original pose and orientation from the input image. This mode allows for more creative camera work while maintaining character consistency. Key applications include:
- Dramatic performances requiring emotional consistency
- Close-up shots where facial expressions are paramount
- Camera movement sequences (pans, tilts, zooms)
- Character-focused narratives with minimal environmental constraints
This mode effectively decouples character orientation from camera perspective, giving creators greater flexibility in cinematic storytelling. The AI focuses on preserving your character's fundamental pose while allowing the virtual camera to move independently.
Step-by-Step Workflow for Professional Results
Preparation: Input Specifications
Successful Kling Motion Control implementation begins with proper input preparation. Follow these guidelines for optimal results:
Reference Video Requirements:
- Duration: 3-30 seconds (sweet spot: 5-15 seconds)
- Resolution: Minimum 720p, recommended 1080p or higher
- Subject Visibility: Full body in frame, no obstructions
- Movement Quality: Clear, continuous motion without cuts or jumps
- Lighting: Consistent illumination, avoid extreme shadows
Character Image Specifications:
- Clarity: High-resolution image with visible facial features
- Pose: Natural standing or action pose matching intended movement
- Background: Simple, uncluttered backgrounds work best
- Lighting: Even lighting without harsh shadows
Process: Upload Reference → Select Mode → Prompt for Environment
-
Upload Reference Video: Begin by selecting a high-quality reference clip that demonstrates the movement pattern you want to replicate. Ensure the subject is clearly visible and the motion is continuous.
-
Choose Orientation Mode: Based on your creative goals, select either Character Orientation Matches Video for environmental consistency or Character Orientation Matches Image for character-focused storytelling.
-
Craft Environment Prompts: Describe the desired setting using specific, evocative language. For example: "A futuristic cityscape at dusk with neon lights reflecting on wet streets" or "A serene forest clearing with dappled sunlight filtering through the canopy."
-
Review and Generate: Preview your settings, then initiate the generation process. The AI will analyze your inputs and create the motion-controlled sequence.
Advanced Camera Control via Prompts

Since Character Orientation Matches Image mode supports independent camera movement, you can achieve sophisticated cinematic effects through strategic prompting:
Pan Shots
Create horizontal camera movements with prompts like:
- "Slow pan from left to right revealing the expansive landscape"
- "Quick pan following the character's movement across the room"
- "Gentle pan establishing the environment before focusing on the subject"
Tilt Movements
Implement vertical camera angles with descriptions such as:
- "Low-angle tilt upward emphasizing the character's stature"
- "High-angle tilt downward creating a sense of vulnerability"
- "Dutch tilt for dramatic, disorienting effect"
Zoom Effects
Control focal length changes with prompts like:
- "Slow zoom-in on the character's expressive face"
- "Crash zoom for sudden dramatic emphasis"
- "Dolly zoom creating vertigo effect"
Tripod Techniques
For stable, professional shots:
- "Static tripod shot with subtle camera breathing"
- "Locked-off camera position with character movement"
- "Steadicam-style smooth following shot"
The "Hidden" Cost of Perfection
While the unit cost is accessible, achieving broadcast-ready quality with Kling Motion Control often requires a "gacha" mindset. Expect to generate 3-5 variations to achieve perfect limb alignment and eliminate artifacts. Common challenges include:
Limb Hallucinations
The AI may occasionally generate extra limbs or incorrect joint positions. This typically occurs when:
- Reference motion contains complex overlapping movements
- Character clothing creates ambiguous silhouettes
- Lighting conditions obscure clear body definition
Temporal Consistency Issues
Maintaining consistent character appearance throughout the sequence can be challenging, particularly with:
- Rapid movement sequences
- Complex fabric dynamics
- Changing lighting conditions
Environmental Integration
Seamlessly blending characters into new environments requires careful prompt engineering and multiple iterations to achieve natural-looking interactions.
Troubleshooting: Common Error Codes

"Upper Body Not Detected"
This error occurs when the AI cannot clearly identify the subject's upper body structure. Common causes include:
Subject Too Small: Ensure your character occupies sufficient frame space (recommended: 60-80% of frame height)
Obstructed Views: Remove any objects blocking the character's upper body
Poor Lighting: Improve illumination to enhance body definition
Complex Backgrounds: Use simpler backgrounds for better detection
Solution: Reshoot reference footage with clearer subject visibility and better lighting conditions.
Camera Drift
When using Character Orientation Matches Image mode, camera drift can occur if prompts lack stability cues:
Problem: Unintended camera movement or shaky footage
Causes:
- Ambiguous movement descriptions
- Conflicting camera instructions
- Lack of stabilization prompts
Fix: Include explicit stabilization language in your prompts:
- "Stable camera position with no movement"
- "Locked-off shot on a tripod"
- "Steady camera following smooth motion"
Best Practices for Optimal Results
Reference Video Selection
Choose reference footage that matches your intended output complexity. For beginners:
- Start with simple walking or standing movements
- Progress to more complex actions as you gain experience
- Avoid reference clips with rapid camera movements initially
Prompt Engineering
Develop a systematic approach to prompt creation:
- Begin with environment description
- Add character action details
- Specify camera behavior
- Include mood and lighting elements
Iterative Refinement
Embrace the iterative nature of AI video generation:
- Generate multiple variations with slight prompt adjustments
- Analyze each result for specific improvement areas
- Build a library of successful prompt combinations
Real-World Applications
Film and Animation Production
Kling Motion Control revolutionizes pre-visualization and animation pipelines by:
- Reducing character animation time from weeks to hours
- Enabling rapid iteration on movement concepts
- Providing realistic motion reference for traditional animators
Game Development
Game studios leverage this technology for:
- Rapid prototyping of character animations
- Creating diverse NPC movement libraries
- Generating cinematic cutscenes efficiently
Educational Content
Educators use motion control for:
- Demonstrating complex physical concepts
- Creating engaging historical reenactments
- Producing interactive learning materials
Future Developments
As Kling Motion Control technology evolves, expect advancements in:
- Multi-character interactions with complex social dynamics
- Enhanced physics simulation for more realistic environmental interactions
- Real-time control interfaces for live performance applications
- Cross-platform compatibility with major animation software
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Digital Puppetry
Kling Motion Control represents a significant leap forward in AI-driven animation technology. By understanding the nuances between Character Orientation Matches Video and Character Orientation Matches Image modes, creators can achieve unprecedented control over their digital characters.
The key to success lies in meticulous preparation, strategic prompt engineering, and embracing the iterative nature of AI generation. While achieving perfection may require multiple attempts, the results—cinematic-quality character animation with realistic movement—are well worth the effort.
As you continue your journey with Kling Motion Control, remember that each generation provides valuable learning opportunities. Document your successful approaches, analyze your challenges, and gradually build your expertise in this exciting new frontier of digital content creation.
Ready to transform your creative workflow? Start experimenting with Kling Motion Control today and discover the power of deterministic AI animation.

Z-Image Turbo Guide: Running Alibaba''s 6B Beast in ComfyUI (Vs. FLUX)
Forget 24GB VRAM. Alibaba''s Z-Image Turbo (6B) delivers photorealistic results and perfect Chinese text in just 8 steps. Here is your complete ComfyUI workflow guide.

Kling 2.6 & Niji 7 Workflow: How to Create Viral AI Anime Dramas (2026 Guide)
Master the ultimate AI anime workflow combining Niji 7's visuals with Kling 2.6's native audio and motion control. A step-by-step guide for creating viral manga dramas.
5 Secret Prompts for Hollywood-Style Cinematic Shots
Struggling with flat lighting? Use these copy-paste prompt formulas to master depth of field and dynamic camera angles.
How to Optimize Seedance 2.0 Costs: A Developer's Guide to 50% Savings
Master the economics of Seedance 2.0 with proven strategies to reduce API costs by 50%. Learn the 'Draft-Lock-Final' workflow and token optimization techniques.
Seedance 2.0 Pricing Revealed: Is the 1 RMB/Sec Cost the Death of Sora 2?
ByteDance's Seedance 2.0 pricing is here: 1 RMB per second for high-quality AI video. Discover how this cost structure challenges Sora 2 and reshapes the industry.

Kling 3.0 is Live: Native Audio & 15s Videos (Plus: ByteDance's Seedance 2.0 Arrives)
Major Update: Kling 3.0 is now live with native audio and 15s duration. Plus, we introduce ByteDance's Seedance 2.0, the new multimodal AI video beast. Try both today.

Kling 3.0 vs Runway Gen-4.5: The Ultimate AI Video Showdown (2026 Comparison)
A comprehensive 2026 comparison. We test Kling 3.0 vs Runway Gen-4.5 (Flagship) and Kling 2.6 vs Gen-4 (Standard). Discover which AI video generator offers the best daily free credits.

Why Seedance 2.0 Was Removed? The Truth Behind StormCrew's Video & Kling 3.0's Defeat
StormCrew's review caused a panic ban of Seedance 2.0. Discover why its 10x cost-effectiveness and distillation tech are crushing Kling 3.0.